4710-97 Street NW, Edmonton, AB
621 North Vickers St, Thunder Bay, ON
1185 Michener Road, Sarnia, Ontario, N7S 4B1
Radiography
What is Conventional Radiography?
Conventional radiography works the same way a bone X-Ray and the technology has been around for a very long time.
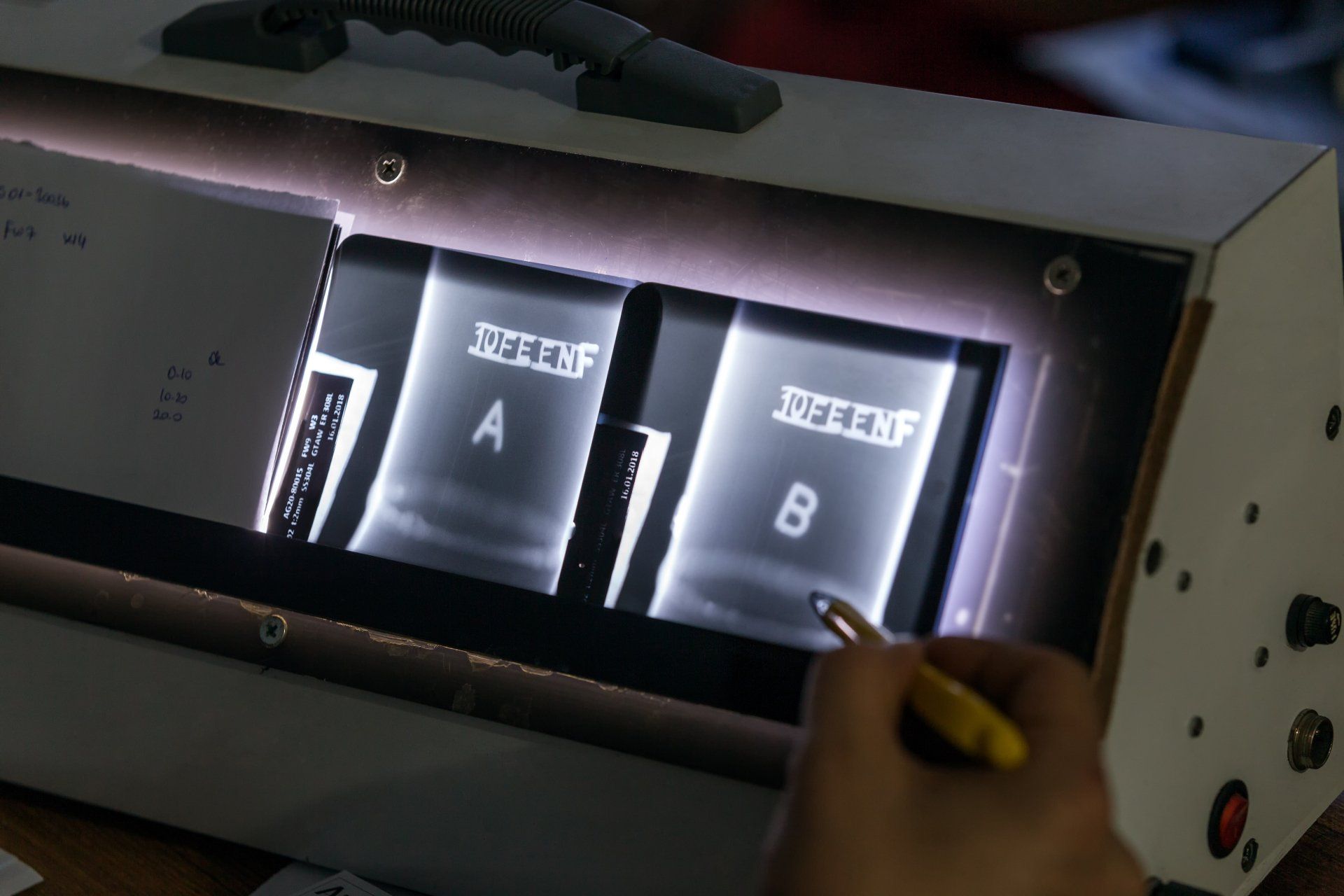
Conventional radiography is the use of a radiation source, and a film that once developed will show internal details about an object.
How does industrial radiography work in conventional NDT?
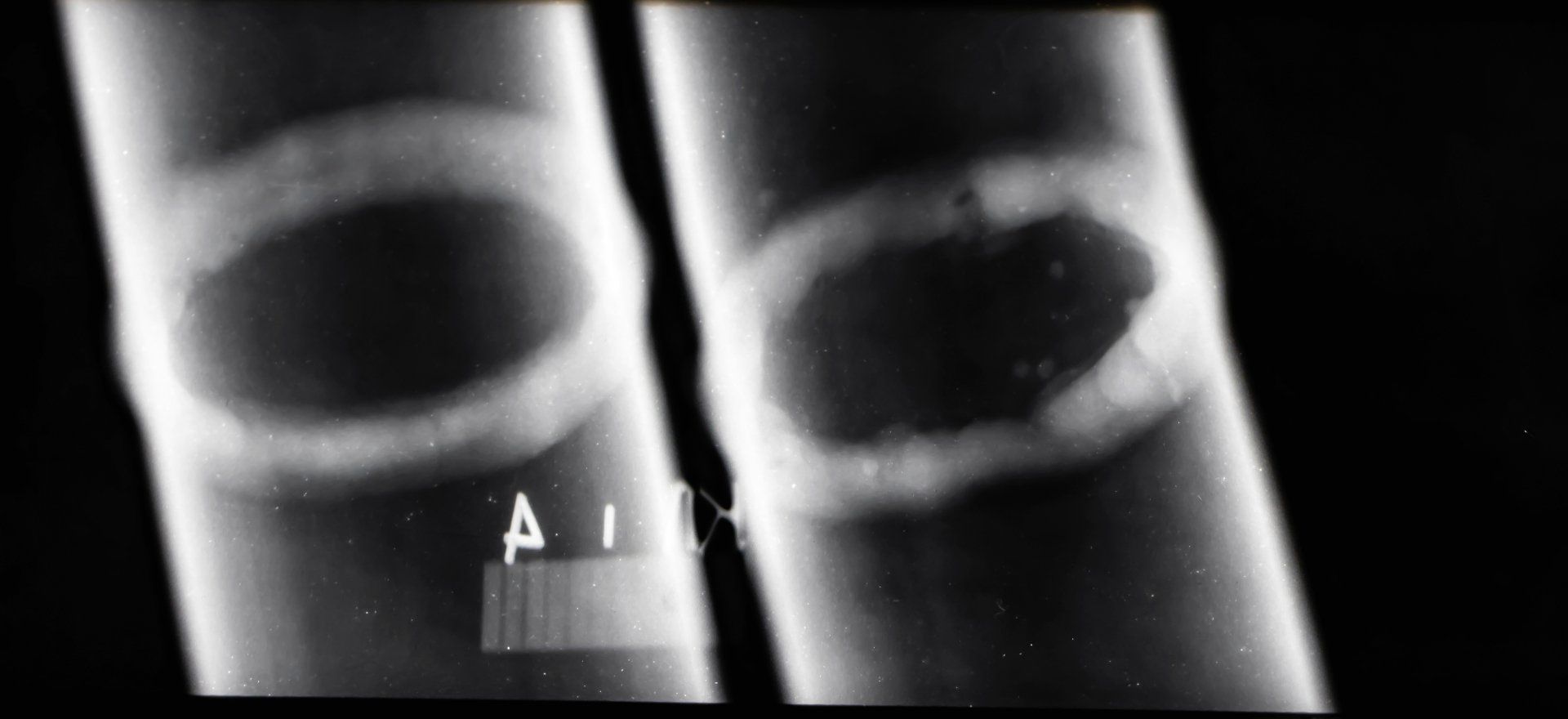
Radiography testing is conducted by a certified exposure device operator (CEDO). They place a part to be tested between a radiation source, and a detector. This will show volume and thickness differences. It is measured by the amount of radiation penetration.
Radiography will find internal or external defects, voids and damage. It is suitable for testing when both sides of welds and joints can be accessed. There is an exception where double-wall pipes require different signal image techniques to be used.
-
X-Ray Radiography (RT)
Learn more →This testing method ends with an image being projected onto a film that needs to be developed.
-
Gamma Radiography
Learn more →A well organized tracking system is in place to ensure that all devices meet fitness for purpose standards when used.
X-Ray Radiography (RT)
This is a type of x-ray radiography using the similar image processing techniques that doctors use for x-rays. Radiographic film and the X-ray source are placed on opposite sides of the material. The film detects exposure to various quantities of radiation received on the film.
This testing method ends with an image being projected onto a film that needs to be developed. Once developed, inspectors with CGSB RT Level 2 / ASNT level 2 certification interpret the results and record the details of any defect present.
Gamma Radiography
The most common radioactive isotope source in use for gamma radiation is Iridium 192. The source used for emitting the radiation need to be frequently replaced as the half life of Iridium is only 74 days. A well organized internal tracking system is in place to ensure that all devices meet fitness for purpose standards when used.
When working with thicker steel cobalt 60 gamma radiography is used. The thickness range for cobalt 60 is between 25 and 200 mm thick. This also has a much longer half life tolerance at 5.26 years.
Advanced Radiography
As technology advances, so do NDT testing techniques. On place this is apparent is with radiography. Where the only methods available previously were x-ray & films, computers and digital sensors are now able to be utilized in many situations.
How does industrial radiography work in Advanced NDT?
Digital radiography is similar to X-Ray radiography, in that the material to be tested is placed between a radiation emitter, and a detector. In the case of Digital Radiography (DR), that detector is a sensor rather than a film. This sensor is able to convert the radiation to an electrical charge, and finally to a digital image.
-
Digital Radiography (DR)
Learn more →We've got the knowledge you need.
-
Computed Radiography (CR)
Learn more →We've got the knowledge you need.
Digital Radiography
Digital Radiography is a form of computed radiography using a low energy X-ray tube. The ray photons are directed towards a Digital Detector Array (DDA) or flat panel detector. The results are a digital image.
This technology offers some advantages over film during inspection tasks. First, the need for consumable costs are removed. Second, there is also a noticeable reduction in the time to produce results.
Computed Radiography
CR is a form of digital radiography that replaces conventional X-ray film with cassettes that use photo luminescence screens to capture the image. Computed Radiography like X-Ray radiography measures thickness differences, voids, etc.
This technology offers reporting, cost, and record keeping advantages for inspection tasks. Examining pipes and other metals will show flaws more quickly. A digital record will be tracked and logged, for further analysis and certification reporting.
621 North Vickers St, Thunder Bay, ON
P7C 4B9
1185 Michener Road,
Sarnia, Ontario, N7S 4B1

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
Slide title
Write your caption hereButton

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
©2021 Copyright | All Rights Reserved | Eagle Eye NDT